Can Fiber Optic Transceiver Be Used As High Speed UART?
With the advancement of communication technologies, greater use of fiber optic transceivers is now used in industrial control, data centers, and long distance communication. At the same time, a serial communication interface known as a universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) is also used extensively in high speed data transfers among embedded systems and microcontrollers. Can fiber optic transceiver be used as high speed UART? You can find the answer in this post. Let’s dive in!
Part 1. What is a Fiber Optic Transceiver?
A fiber optic transceiver changes optical signals to electrical signals and vice versa which means that their respective signals are encoded and decoded in optic and electrical format. This function is critical in Ethernet networks as well as in industrial process controls and long-range data transfers.
It seamlessly integrates electronic and optical transmitting and receiving components which are then used to capture the data in its electrical format, thus ensuring high speed and high distance communication which is always a challenge when using a standard copper cable.
Some of the popular fiber optic transceiver types are:
- SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable): Compact, hot-swappable transceiver commonly found in networking devices.
- SFP+ (Enhanced SFP): An upgraded SFP with higher data rates, typically up to 10 Gbps.
- QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable): Transceiver of high density with numerous lanes to handle extremely high-speed data transfer, widely used in data centers.
In essence, the main function of a fiber optic transceiver is to serve as a conduit between optical and electrical communications to enable efficient, reliable, and extensive data transmission.
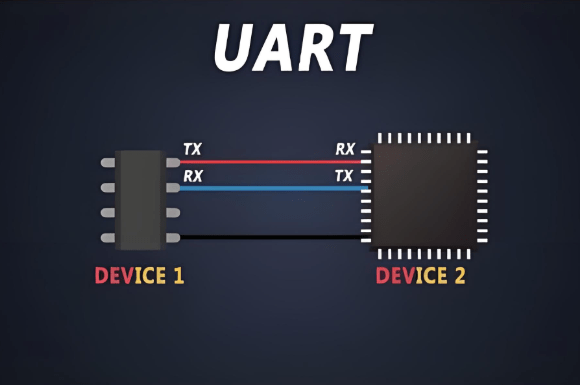
Part 2. What is UART and High-Speed UART?
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a paradigm of a serial protocol for communication and data is transferred and received on two signal wires as on ‘TX’ (transmit) and ‘RX’ (receive) ports. Unlike synchronous communication techniques , UART does not require the provision of a common clock signal and is therefore very easy and convenient for use in microcontroller systems , embedded systems , and in connection to peripherals.
Descriptions of high-speed UART indicate its use with baud rates ranging from 1 Mbps to over 12 Mbps, exceeding those speeds depending on supported hardware. Such exotic speeds may be more relevant in high-end sensors, contemporary control systems, or multimedia embedding, where rapid data interchange is the dominant requirement.
But UART signals are usually TTL-level, i.e., 3.3V or 5V voltage levels, whereas fiber optic transceivers handle differential signals such as LVDS (Low-Voltage Differential Signaling) or RS-485. This difference in the nature of signal and electrical nature means that direct connection between a standard UART interface and a fiber optic transceiver is not straightforward, and some sort of conversion or interfacing circuitry is required for compatibility.
Part 3. Can Fiber Optic Transceiver be Used As High Speed UART?
In principle, a fiber optic transceiver can transmit any digital signal. However, using it directly in UART communication has a number of technical problems:
Voltage Level Mismatch
Single-ended TTL voltage levels (3.3V or 5V) are utilized in standard UART signals, whereas fiber optic transceivers typically interface with differential signals such as LVDS or RS-485. Direct connection may lead to signal distortion, data errors, or complete communication failure.
Baud Rate and Timing Issues
Fast UART requires precise timing control for guaranteed seamless data transfer. Some fiber optic transceivers have internal buffering, encoding, or clock recovery capabilities, which introduce latency or jitter and may interfere with the real-time characteristic required by UART.
Signal Conversion Requirements
In practical application, there normally needs to be a Fiber-to-UART converter. It converts UART signals to a fiber-compatible form for transfer over optical fiber and converts them back into UART signals when received.
Such converters deliver signal integrity, proper voltage levels, and timing, which gives fiber-optic UART communication reliability and fault tolerance over long distances.
While fiber optic transceivers are very flexible, an allocation to a UART interface is not generally possible without appropriate signal conversion and interfacing.
Part 4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Fiber Optics for UART Transmission
Conveying UART signals over fiber optic results in a mechanism to expand communication and signal dependability distances, most notably in electrically hostile or industrial settings. This approach also brings additional costs and complexity of design, however, that needs to be considered.
Advantages:
Enables Long-Distance Transmission – Fiber optic links can carry data kilometers without signal loss, much greater distances than the conventional copper UART links.
Robust Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) – Optical fibers are immune to electrical noise, and as such, they can be applied in industrial and data center environments.
Friendly to Harsh Environments – Their resistance to EMI and environmental factors makes fiber optics ideal for industrial control systems, remote monitoring, and high-speed data centers.
Disadvantages:
Increased Expense – Supporting the fiber optic UART incurs additional costs pertaining to the increased quantity of converters and specialized transceivers required relative to the more conventional copper connections.
Complicated Interfacing – The system’s complexity attributable to differential signaling, as well as the need for system conversion cables, power and connectors, is increased.
Possibly Adverse Effect on Real-Time Capability – The subtle internal coding or buffering of the fiber transceivers transceivers produces spring jitter, which can be rather problematic for the more sensitive types of UART communications.
Part 5. Practical Application Scenarios of Using Fiber Optics Transceiver for UART Communication
The performance quote and the versatility of fiber optics are especially important in circumstances where the serial links of the system are too long and/or there is considerable interference.
In such cases, the associated systems can maintain long-range, high-speed connectivity using fiber optics transceivers and UART converters.
Remote Debugging of Embedded Systems
In long-distance scenarios where embedded systems must be debugged or monitored, fiber optics can substitute standard serial cables for secure remote access and ensure that signal strength is maintained. This is especially advantageous for field-deployed hardware or systems in remote and difficult-to-access areas.
Industrial Automation and Control
Optical fiber links ensure strong immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are thus well suited for installation in highly industrial environments where motors, heavy machinery, or high-power devices might interfere with UART communications in the normal course. This assures safe and accurate data transfer to industrial control systems.
Data Center and Remote Device Communication
In data centers and networks of remote devices, fiber optics facilitate swift and stable data transmission, permitting long-range connections between switches, servers, and other devices in a network. This aids in the reliable communication in high congestion zone.

In Summary
Fiber optic transceivers, in principle, can be used for UART communication at high speeds, but they cannot directly be interfaced. A Fiber-to-UART converter or an interposing interface must be implemented so that voltage levels and signal characteristics may be translated.
For embedded engineers and industrial users, selection of the proper type of fiber optic transceiver and UART converter is crucial in order to achieve reliable and high-speed serial communication.
FAQs
Is UART a Transceiver?
No, UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is not a transceiver. It is a serial communications protocol and hardware module that provides parallel-to-serial data conversion and transmission (TX) and reception (RX) of digital signals.
While it does support transmit and receive functions, it does not include the optical or electric signal conversion functions provided by a transceiver.
What are Fiber Optic Transceivers Used For?
Fiber optic transceivers are used to translate optical signals to electrical signals and send them over fiber optic cable, and vice versa when received.
They are widely used in telecommunication networks, data centers, industrial control, and long-distance networking and utilized to enable high-speed, reliable, EMI-immune transmission over distances copper connections cannot achieve.
Is Fiber Optic Cable Used for High-Speed Wired Communication?
Yes, fiber optic cables are extensively used for high-speed wired communications. As they transfer data as light waves, they support very high bandwidth and long distance with hardly any signal loss.
Fiber optic cables are optimally applied to internet backbones, data centers, enterprise networking, and industrial applications where high-speed, reliable, and interference-free communication is required.








